At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Is the Posterior Hypothalamus?
The posterior hypothalamus is the back end part of the hypothalamus region of the brain. It is a compact cluster of neurons called nuclei. Its primary function is to regulate body heat, specifically to warm the body up when it is cold. Any damage to the posterior hypothalamus is likely to impair its ability to do this. It is found in a similar region in the brains of all vertebrates such as humans and dogs.
Towards the bottom-center of the brain is the hypothalamus. Not surprisingly, it is located directly below the thalamus and is bounded by the pituitary gland and the cerebellum. It is almond-sized and regulates metabolic activity. This means its most important function is homeostasis, the maintenance of an equilibrium or status quo throughout the body.

The hypothalamus first receives data from the body and other parts of the brain regarding various aspects of the body. It then uses the data to formulate and execute a response. Each part of the thalamus produces a response in order to regulate a specific area of the body. These include blood pressure, heat, fluid and electrical balances within the body.
A posterior hypothalamus is also called the posterior nucleus of the hypothalamus. It performs the opposite function of the anterior hypothalamus. It is composed of a dense amount of neuron or nerve cells that compose the brain.

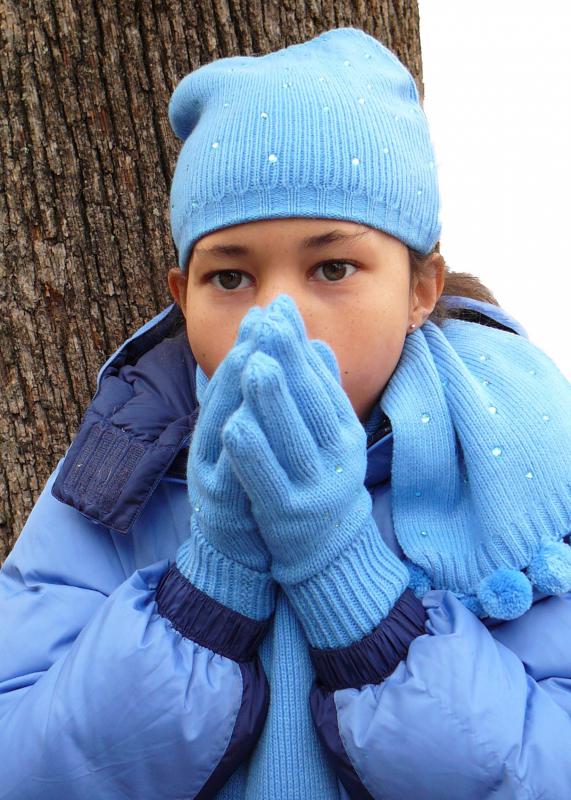
The function of the posterior hypothalamus is to regulate body heat. Its specific role in this is to warm the body up as opposed to the anterior hypothalamus that is designed to cool the body. Heat regulation varies from species to species and also depends if the animal is warm- or cold-blooded. For example, humans can sweat to cool down, but dogs must pant.

The posterior hypothalamus uses the tools at its disposal to warm the body. The human hypothalamus has five main ways of achieving this. First, the body can shiver, then it can increase the heart rate and then it can increase the metabolic rate. Fourth, it can mobilize the body’s carbohydrate reserve, and fifth, it can increase blood pressure by narrowing the blood vessels in a process known as cutaneous vasoconstriction.

Damage to the posterior hypothalamus naturally causes the body to be less able to warm itself. This can either prevent the hypothalamus receiving the correct data about the body’s heat or it can prevent it from responding to a problem. This will cause hypothermia, as the body will be unable to raise its own heat.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:














Discuss this Article
Post your comments